In this EM Cases episode on Pediatric Procedural Sedation with Dr. Amy Drendel, a world leader in pediatric pain management and procedural sedation research, we discuss how best to manage pain and anxiety in three situations in the ED: the child with a painful fracture, the child who requires imaging in the radiology department and the child who requires a lumbar puncture. Without a solid understanding and knowledge of the various options available to you for high quality procedural sedation, you inevitably get left with a screaming suffering child, upset and angry parents and endless frustration for you. It can make or break an ED shift. With finesse and expertise, Dr. Drendel answers such questions as: What are the risk factors for a failed Pediatric Procedural Sedation? Why is IV Ketamine preferred over IM Ketamine? In what situations is Nitrous Oxide an ideal sedative? How long does a child need to be observed in the ED after Procedural Sedation? Do children need to have fasted before procedural sedation? What is the anxiolytic of choice for children requiring a CT scan? and many more…
Written Summary & blog post by Michael Kilian, edited by Anton Helman, February 2016
Cite this podcast as: Drendel, A, Helman, A. Pediatric Procedural Sedation. Emergency Medicine Cases. February, 2016. https://emergencymedicinecases.com/pediatric-procedural-sedation/. Accessed [date].
This Pediatric Procedural Sedation episode is paired with Episode 67 Pediatric Pain Management
Bridging Analgesics: Triage to Procedural Sedation
Your initial approach to pain control when the patient hits the ED door will depend on severity of pain. For presentations of severe pain, intranasal fentanyl is a recommended first line agent as it is fast and easy to administer, avoids requiring cooperation with oral medications, and provides reliable analgesia that has been shown to be equivalent to intravenous morphine. For mild to moderate pain, consider oral agents such as ibuprofen, which has been shown to be more effective than acetominophen for pain control in orthopedic injuries in children.
Intranasal (IN) Fentanyl
A general rule of thumb for dosing IN fentanyl is twice the IV dose.
Tips to increase your success with intranasal fentanyl and other IN medications:
- Avoid intranasal medications in children with obviously congested nares since absorption will decrease and dosing will be unreliable
- Choose the highest concentration formulation of fentanyl as this will allow you to use a smaller volume
- Use BOTH nostrils for volumes over 0.3 ml to double the absorptive surface and reduces runoff
- Consider administering an oral analgesic concurrently for continued pain management after the Fentanyl has worn off
- Respiratory depression is rare with correct dosing, however naloxone is also effective intranasally, if needed, as a reversal agent
- Instruct the child to take deep breath in “like smelling a flower”
For guidance around use of intranasal medications we recommend www.intranasal.net. This resource provides evidence-based recommendations for a variety of applications of intranasal medication including pain control, sedation and seizure management.
Distraction Techniques for Pediatric Procedural Sedation
There is good evidence to support the use of distraction techniques to help decrease the child’s anxiety and pain experience during a procedure. Familiar faces and various technological devices such as smartphones and tablets may be effective at calming the child and can help move things along more smoothly.
See Episode 67 Pediatric Pain Managment for a more in-depth discussion on Distraction Techniques
Assessment for Pediatric Procedural Sedation
As in the adult population, every procedural sedation must begin with a focused history to help you plan your sedation. Any history of procedural sedation and details surrounding their experience and effects will be important in planning which agents you employ. In the past medical history, be sure to screen specifically for asthma, viral respiratory infections and obstructive sleep apnea as these are important risk factors for complications. Reviewing the allergies and potential medication interactions will also influence what agents you use. Perform a thorough physical exam for high risk airway features as well as cardiorespiratory exam.
Is Fasting Required Prior to Pediatric Procedural Sedation?
It is helpful to know when the patient had their last meal but there is not a lot of research that supports mandatory fasting to prevent complications of aspiration in procedural sedation. A large study addressing this question found no difference in adverse events in children who had been fasting 2, 4, 6 or 8 hours. A conservative approach based on The American Society of Anesthesiologists fasting guidelines would be to wait 3-4 hours after their last meal but there is no indication to wait if you need to urgently perform a procedure.
Emesis is a known side effect of ketamine. There is evidence to support the use of ondansetron in conjunction with ketamine to reduce the risk of emesis (NNT= 9) . If you are really concerned about the risk of vomiting, consider using propofol for your sedation as it has a lower risk of vomiting with subsequent aspiration than ketamine.
Preparation for Pediatric Procedural Sedation
Remember that anatomical differences in children compared to adults, render them more prone to airway obstruction.
Perform an equipment check to ensure that the following equipment is working:
- Cardiovascular monitoring
- Pulse oximetry
- Capnography (has been shown to detect apnea sooner than pulse oximetry; if capnography is not available use direct visualization of the chest wall to monitor for apnea)
Position the child appropriately (avoid supine position when possible) in a monitored setting and have extra help available in the room. Ideally, one nurse dedicated to monitoring the vital signs of the child.
A study by Grunwell et al. of 8000 children identified risk factors for a failed pediatric sedation (hypoxia or apnea) outside the operating room:
- Obesity
- Sleep apnea or history of snoring
- Age > 7 years
- History of upper respiratory tract infection
- American Society of Anesthesiologists class 2 or greater
Family Presence During Pediatric Procedural Sedation
The EM literature has shown over and over that families prefer staying at the bedside for procedures. Parents use of distraction techniques with music or videos from smartphones or tablets, and even helping out in the procedure can improve partental satisfaction and decrease the child’s anxiety. So generally speaking it’s a good idea to have mom or dad at the bedside helping out. However, we’ve all been in the situation when mom or dad starts freaking out during the procedure – and usually we can anticipate which family members will react this way – so for those folks, you may elect to ask them to step out of the room during the procedure.
Medications for Pediatric Procedural Sedation
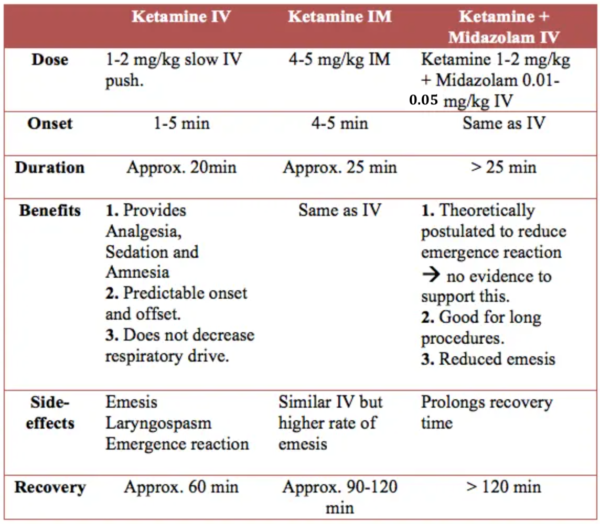
Ketamine
Ketamine has become the most common agent for pediatric procedural sedation. It provides the desired trifecta of analegesia, sedation and amnesia in one single agent. Some routes and combinations are described in the following table.
IV Ketamine is generally preferred over IM Ketamine. IM Ketamine has a longer recovery period, a higher rate of emesis and is also difficult to titrate if more sedation needed.
Rapid push dose of IV Ketamine at 0.8mg/kg as an alternative to slow IV push Ketamine, has been evaluated by Chinta et al. in a pilot study of 20 children. The preliminary data are encouraging as the success of adequate sedation and adverse reactions seen were comparable to the standard dose and slow IV push while having a shorter recovery time. However, rapid push dose IV ketamine can not be recommended for pediatric procedural sedation until a large validated RCT has shown definite results.
Benzodiazepines are useful for treating the rare emergence reactions that are associated with Ketamine, but they do not decreased the likelihood of an emergence reaction occurring. Furthermore, co-administration of midazolam increases the risk of respiratory complications even though the risk of emesis is reduced.
Contraindications to ketamine
- Age
- Increased risk of respiratory complications
- Animal studies suggest NMDA antagonists are associated with apoptosis and neuro-degeneration in developing brains
- History of schizophrenia/psychotic disorder
Etomidate
Etomidate has been shown to be safe for procedural sedation in the pediatric population. Its’ benefits include a favorable hemodynamic profile and short duration of action. Consider how much time you anticipate the procedure to last, as Etomidate is best suited for short procedures.
Etomidate Dosing for pediatric procedural sedation: 0.1 to 0.2 mg/kg slow IV push
Propofol
The risks of respiratory depression with Propofol are much higher than with Ketamine. In addition, Propofol does not have any analgesic properties and so it is recommended that it be combined with an analgesic such as fentanyl.
Dosing for pediatric procedural sedation: 0.5-1mg/kg slow IV push
Fentanyl +Midazolam
A combination of fentanyl and midazolam used to be a popular cocktail for procedural sedation. This combination is no longer recommended as it has been associated with a high incidence of adverse events including respiratory depression and apnea.
Nitrous Oxide (NO)
Nitrous oxide is weak dissociative anaesthetic and it gives a rapid, reliable change in depth of analgesia and sedation with a rapid recovery. Effective analgesia can often be obtained with local lidocaine or regional nerve blocks but still require a calm and sedated child to complete the procedure. Nitrous oxide is especially well suited for the patient who requires more anxiolysis than pain control. Examples of procedures where Nitrous oxide would be a reasonable option include genital lacerations and reduction of forearm fractures. Studies have shown that nitrous oxide sedation, in conjunction with a hematoma block for forearm fractures, was just as effective as IV ketamine and midazolam, AND had a faster recovery time.
Dosing: Nitrous oxide is delivered by nebulizer via a gas system, usually 50% NO as a baseline dose. Some machines will allow you to adjust the percentage of nitrous the patient is inhaling so you can titrate the depth of sedation. You can add an opioid or benzodiazepine to achieve a deeper sedation.
Time of onset: approximately 3-5 min
Recovery: approximately 3-5 min
Update 2017: A Canadian prospective multicentre observational study examined incidence and risk for serious adverse events in pediatric procedural sedation. They found ketamine alone was associated with the best outcomes, resulting in significantly fewer serious adverse events and interventions than ketamine combined with propofol or fentanyl. Abstract
How long does a child need to be observed in the ED post-procedural sedation?
The effects and duration of each sedative agent will depend on dosing, route of administration and the patient’s metabolism of the drug(s). In terms of assessing a child for safe discharge home, they should be able to walk by themselves, tolerate oral fluids without emesis and have reliable caregivers at home who can monitor them closely. The TREKK guidelines published the following recommendation: “Monitor until the patient is able to perform their baseline (developmentally appropriate) activities (speech, motor, cognitive) as well as tolerate oral intake.”
Pediatric Sedation for Diagnostic Imaging
For non-painful procedures, distraction should be attempted before medications are administered. Some departments are equipped with visual equipment that can distract children in the radiology department.
If distraction techniques are ineffective, IN midazolam is recommended as first line therapy for sedation. If IN midazolam is not available, oral midazolam is recommended.
- Intranasal dose: 0.3mg/kg (max 10mg); time of onset: 7-10min
- Oral dosing: 0.7mg/kg (max 20mg); time of onset: 15-20min
Before administering midazolam, consider the recovery time and that it may cloud your physical and neurological assessments of the patient. Perform a good neurological exam before the sedation!
Pediatric Procedural Sedation for Lumbar Puncture
An important intervention to maximize the chances of success with lumbar puncture is adequate local pain control. Anesthetizing the skin with topical lidocaine (LMX 4%) can be helpful in this regard without having to resort to the discomfort of injected lidocaine. LMX has an onset within 30mins with reliable anesthetic effect at about 7 minutes, and was shown to increase success of lumbar puncture in a two prospective observational studies of 428 and 1,474 patients.
Local pain control, along with distraction techniques can often obviate the need for systemic sedation. For young infants who cannot be distracted, Surcose has been shown to be an effective sedative. Sucrose can often achieved the desired level of sedation such that other less safe medications are not required in young infants
Medications of choice for sedation for lumbar puncture
< 6months old: sucrose
6months – 5 years: IN midazolam (or oral midazolam if IN is not available)
> 5 years: inhaled nitrous oxide or midazolam
Additional Resources
For the TREKK Summary and Recommendations for procedural sedation please visit: http://trekk.ca/resources?tag_id=D016292
EM Cases guest experts Samina Ali and Amy Drendel’s latest paper on Procedural Sedation Ali S, Mcgrath T, Drendel AL. An Evidence-Based Approach to Minimizing Acute Procedural Pain in the Emergency Department and Beyond. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2016;32(1):36-42. Abstract http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26720064
EMCrit’s review of ACEP Procedural Sedation Update for 2013
For more on Paediatric Emergencies download our free interactice eBook EM Cases Digest Vol. 2 Pediatric Emergencies
References
Rickard C, O’meara P, Mcgrail M, Garner D, Mclean A, Le lievre P. A randomized controlled trial of intranasal fentanyl vs intravenous morphine for analgesia in the prehospital setting. Am J Emerg Med. 2007;25(8):911-7. Abstract
Practice guidelines for preoperative fasting and the use of pharmacologic agents to reduce the risk of pulmonary aspiration: application to healthy patients undergoing elective procedures: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Committee on Standards and Practice Parameters. Anesthesiology. 2011;114(3):495-511. Full Article http://anesthesiology.pubs.asahq.org/article.aspx?articleid=1933410
Godwin SA, Burton JH, Gerardo CJ, et al. Clinical policy: procedural sedation and analgesia in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 2014;63(2):247-58.e18. Full PDF http://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(13)01489-3/pdf
Grunwell JR, Mccracken C, Fortenberry J, Stockwell J, Kamat P. Risk factors leading to failed procedural sedation in children outside the operating room. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2014;30(6):381-7. Abstract http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24849275
Roback MG, Bajaj L, Wathen JE, Bothner J. Preprocedural fasting and adverse events in procedural sedation and analgesia in a pediatric emergency department: are they related?. Ann Emerg Med. 2004;44(5):454-9. Abstract http://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(04)00282-3/abstract
Green SM, Roback MG, Krauss B, et al. Predictors of emesis and recovery agitation with emergency department ketamine sedation: an individual-patient data meta-analysis of 8,282 children. Ann Emerg Med. 2009;54(2):171-80.e1-4. Abstract http://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(09)00372-2/abstract
Langston WT, Wathen JE, Roback MG, Bajaj L. Effect of ondansetron on the incidence of vomiting associated with ketamine sedation in children: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2008;52(1):30-4. Abstract http://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(08)00364-8/abstract
Chinta SS, Schrock CR, Mcallister JD, Jaffe DM, Liu J, Kennedy RM. Rapid administration technique of ketamine for pediatric forearm fracture reduction: a dose-finding study. Ann Emerg Med. 2015;65(6):640-648.e2. Abstract http://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(14)01579-0/abstract
Luhmann JD, Schootman M, Luhmann SJ, Kennedy RM. A randomized comparison of nitrous oxide plus hematoma block versus ketamine plus midazolam for emergency department forearm fracture reduction in children. Pediatrics. 2006;118(4):e1078-86. Abstract
Migita RT, Klein EJ, Garrison MM. Sedation and analgesia for pediatric fracture reduction in the emergency department: a systematic review. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2006;160(1):46-51. Full Article http://archpedi.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=204423
Roback MG, Wathen JE, Bajaj L, Bothner JP. Adverse events associated with procedural sedation and analgesia in a pediatric emergency department: a comparison of common parenteral drugs. Acad Emerg Med. 2005;12(6):508-13. Full PDF http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1197/j.aem.2004.12.009/epdf
Wathen JE, Roback MG, Mackenzie T, Bothner JP. Does midazolam alter the clinical effects of intravenous ketamine sedation in children? A double-blind, randomized, controlled, emergency department trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2000;36(6):579-88. Abstract http://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(00)47787-5/abstract
Zier JL, Liu M. Safety of high-concentration nitrous oxide by nasal mask for pediatric procedural sedation: experience with 7802 cases. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2011;27(12):1107-12. Abstract http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22134227
Stevens B, Yamada J, Lee GY, Ohlsson A. Sucrose for analgesia in newborn infants undergoing painful procedures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;1:CD001069. Full PDF http://apps.who.int/rhl/reviews/cd001069.pdf?ua=1
Deasy C, Babl FE. Intravenous vs intramuscular ketamine for pediatric procedural sedation by emergency medicine specialists: a review. Paediatr Anaesth. 2010 Sep;20(9):787-96. Abstract http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20716070
Dr. Helman, Dr. Kilean & Dr. Drendel have no conflicts of interest to declare

For more EM Cases content on Pediatric Emergencies check out our free interactive eBook,
EM Cases Digest Vol. 2 Pediatric Emergencies here.
Now test your knowledge with a quiz.






I have been listening to your podcast for a few years now, Anton and find it pretty much No 1 in the FOAM universe… What makes it to stand out – is that you have true world experts in the field in your episodes, you and your guests do not sound like cheap sales people peddling dodgy goodies. Your podcasts are very, very comprehensive and pretty much turn any topic inside out… Great show… Anyway…
The paediatric sedation podcast was pretty much a complete package and I truly enjoyed listening it having taken away a few pearls for myself. The only thing I though that would also be of value was to mention that if you do a procedure with the agent that requires prolonged recovery (i.e. ketamine, propofol) on a child, and the procedure is late in the day, say 5-7pm, often kids take a lot longer to wake up and often they just carry on sleeping into the night. I guess this is because their biological clock tells the brain: “it is night time and therefore it is time for the night sleep” and they just carry on. Considering that discharge criteria are a walking, talking, non-vomiting child, who verbalises wants and needs and is back to their pre-procedure LOC – it just does not happen if they are to wake up in the evening…
Thanks again for an exemplary show… Love it!
[…] Helman interviews Dr. Amy Drendel about Pediatric Procedural Sedation. This episode is packed full of useful pearls. […]